$ npm install callsite-record
callsite-record
Create fancy log entries for errors and function call sites.
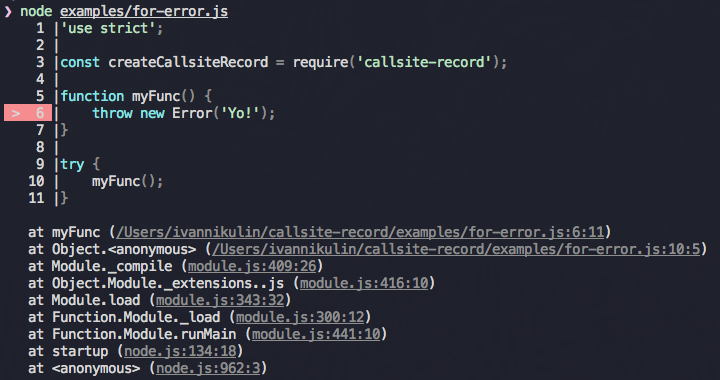
For Error:
'use strict';
const createCallsiteRecord = require('callsite-record');
function myFunc() {
throw new Error('Yo!');
}
try {
myFunc();
}
catch(err) {
console.log(createCallsiteRecord({ forError: err }).renderSync());
}
⬇
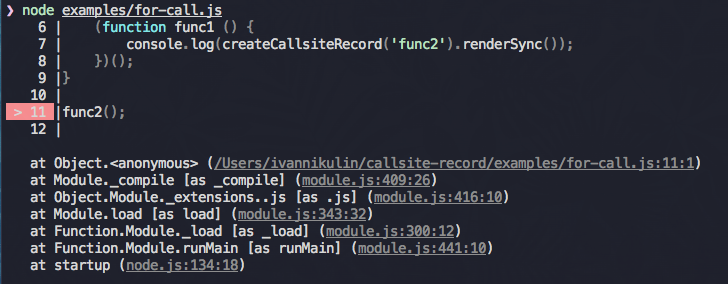
For function call up in the stack:
'use strict';
const createCallsiteRecord = require('callsite-record');
function func2 () {
(function func1 () {
console.log(createCallsiteRecord({ byFunctionName: 'func2' }).renderSync());
})();
}
func2();
⬇
Additional goodies:
- Use renderers for different output formats, e.g. to produce output in HTML.
- Use stack filter to produce clean and beautiful stacks, e.g. removing Node lib internal calls.
Install
npm install callsite-record
API
createCallsiteRecord( { forError, isCallsiteFrame, processFrameFn }) → CallsiteRecord
You can generate a callsite for any stack frame, not only the topmost one. Use the isCallsiteFrame function to select
a frame. This function is called for each frame starting from the top. Return true for the desired frame to generate
the callsite.
Example:
const createCallsiteRecord = require('callsite-record');
try {
throw new Error("We're doomed");
}
catch(err) {
const record = createCallsiteRecord({ forError: err });
}
createCallsiteRecord({ byFunctionName, typeName, processFrameFn }) → CallsiteRecord
Creates CallsiteRecord for the function up in the call stack specified by byFunctionName. You can optionally specify a
typeName if the function is a method. If the function is a constructor set byFunctionName to constructor.
Example:
const createCallsiteRecord = require('callsite-record');
(function func1() {
(function func2() {
(function func3() {
const record = createCallsiteRecord({ byFunctionName: 'func2' });
})();
})();
})();
You can specify processFrameFn function, which will process every frame in callstack. It's usefull when you need to
enable frame processing like source-maps-support.
Example:
const createCallsiteRecord = require('callsite-record');
const wrapCallSite = require('source-map-support').wrapCallSite;
try {
throw new Error("We're doomed");
}
catch(err) {
const record = createCallsiteRecord({ forError: err, processFrameFn: wrapCallSite });
}
(function func1() {
(function func2() {
(function func3() {
const record = createCallsiteRecord({ byFunctionName: 'func2', processFrameFn: wrapCallSite });
})();
})();
})();
CallsiteRecord
CallsiteRecord.render([renderOptions]) → Promise<String>
Renders call site record to the string.
Example:
record.render().then(str => console.log(str));
CallsiteRecord.renderSync([renderOptions]) → String
Sync version of the CallsiteRecord.render.
renderOptions.frameSize
Specifies the number of lines rendered above and below the call site in the code frame. Default: 5.
Example:
console.log(record.renderSync({ frameSize: 0 }));
// > 12 | func1();
// ...
console.log(record.renderSync({ frameSize: 1 }));
// 11 |(function func2() {
// > 12 | func1();
// 13 |})();
// ...
renderOptions.codeFrame
Specifies if code frame should be rendered. If disabled only stack will be rendered. Default: true.
renderOptions.stack
Specifies if stack trace should be rendered in addition to the code frame. Default: true.
renderOptions.stackFilter
Function that will be used to filter stack frames. Function accepts 2 arguments:
stackFrame- stack entry.idx- index of the frame.isV8StackFrame- iftruethenstackFrameis a V8 CallSite object. Otherwise it's a StackFrame object.
Default: null.
Example:
const sep = require('path').sep;
// Remove node core lib calls from the stack trace
record.renderSync({ stackFilter: frame => frame.getFileName().indexOf(sep) > -1 });
renderOptions.renderer
Specifies the output format of the rendering. Default: renderers.default. You can pass your own
renderer object (example implementations) or use
one of the built-in renderers:
renderers.default
Provides ANSI-colored output as shown above.
Usage:
const defaultRenderer = require('callsite-record').renderers.default;
record.renderSync({ renderer: defaultRenderer });
renderers.noColor
Same as default renderer but without colors.
Usage:
const noColorRenderer = require('callsite-record').renderers.noColor;
record.renderSync({ renderer: noColorRenderer });
renderers.html
Outputs HTML that can be later decorated with the CSS and embeded into the web page. Example output.
Usage:
const htmlRenderer = require('callsite-record').renderers.html;
record.renderSync({ renderer: html });
Related
- is-es2016-keyword - Determine if string is an ES2016 keyword.
- highlight-es - Highlight ECMAScript syntax for the console or any other medium.
Author
Ivan Nikulin (ifaaan@gmail.com)
Current Tags
- 4.1.5 ... latest (2 years ago)
19 Versions
- 4.1.5 ... 2 years ago
- 4.1.4 ... 3 years ago
- 4.1.3 ... 7 years ago
- 4.1.1 ... 7 years ago
- 4.1.0 ... 7 years ago
- 4.0.0 ... 8 years ago
- 3.2.2 ... 8 years ago
- 3.2.1 ... 8 years ago
- 3.2.0 ... 8 years ago
- 3.1.0 ... 9 years ago
- 3.0.2 ... 9 years ago
- 3.0.1 ... 9 years ago
- 3.0.0 ... 9 years ago
- 2.0.2 ... 9 years ago
- 2.0.1 ... 9 years ago
- 2.0.0 ... 9 years ago
- 1.0.2 ... 9 years ago
- 1.0.1 ... 9 years ago
- 1.0.0 ... 9 years ago
- @devexpress/error-stack-parser ^2.0.6
- @types/lodash ^4.14.72
- callsite ^1.0.0
- chalk ^2.4.0
- highlight-es ^1.0.0
- lodash 4.6.1 || ^4.16.1
- pinkie-promise ^2.0.0
- eslint ^1.10.3
- mocha ^10.2.0
- publish-please ^5.5.2
