$ npm install n -g
n – Interactively Manage Your Node.js Versions
Node.js version management: no subshells, no profile setup, no convoluted API, just simple.
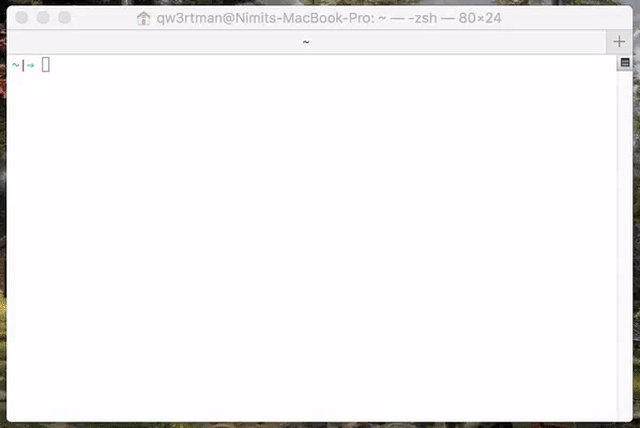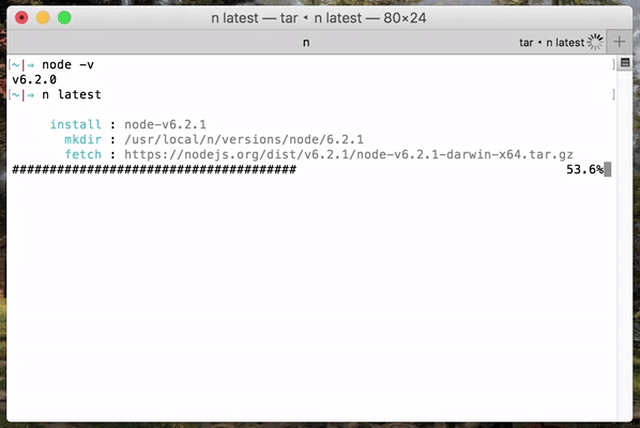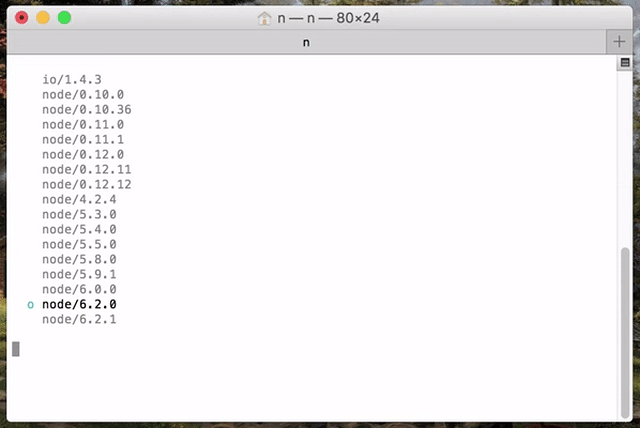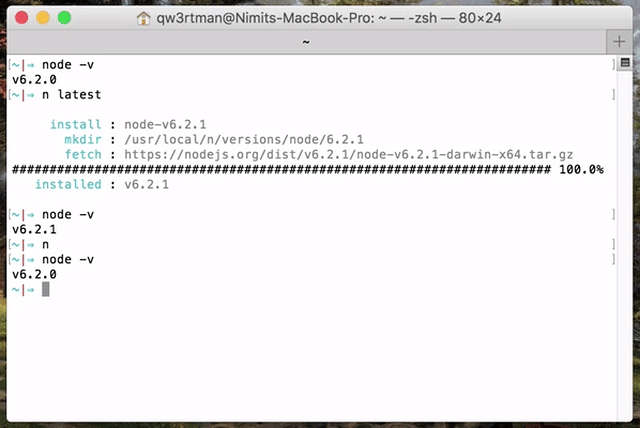
(Note: n is not supported natively on Windows.)
Installation
Since you probably already have node, the easiest way to install n is through npm:
npm install -g n
Alternatively, you can clone this repo and
make install
to install n to bin/n of the directory specified in the environment variable $PREFIX, which defaults to /usr/local (note that you will likely need to use sudo). To install n in a custom location (such as $CUSTOM_LOCATION/bin/n), run PREFIX=$CUSTOM_LOCATION make install.
Once installed, n caches node versions in subdirectory n/versions of the directory specified in environment variable N_PREFIX, which defaults to /usr/local; and the active node version is installed directly in N_PREFIX.
To avoid requiring sudo for n and npm global installs, it is suggested you either install to your home directory using N_PREFIX, or take ownership of the system directories:
# make cache folder (if missing) and take ownership
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/n
sudo chown -R $(whoami) /usr/local/n
# take ownership of node install destination folders
sudo chown -R $(whoami) /usr/local/bin /usr/local/lib /usr/local/include /usr/local/share
Third Party Installers
On macOS with Homebrew you can install the n formula.
brew install n
On Linux and macOS, n-install allows installation directly from GitHub; for instance:
curl -L https://git.io/n-install | bash
n-install sets both PREFIX and N_PREFIX to $HOME/n, installs n to $HOME/n/bin, modifies the initialization files of supported shells to export N_PREFIX and add $HOME/n/bin to the PATH, and installs the latest LTS node version.
As a result, both n itself and all node versions it manages are hosted inside a single, optionally configurable directory, which you can later remove with the included n-uninstall script. n-update updates n itself to the latest version. See the n-install repo for more details.
Installing Node Versions
Simply execute n <version> to download and install a version of node. If <version> has already been downloaded, n will install from its cache.
n 10.16.0
n lts
Execute n on its own to view your downloaded versions, and install the selected version.
$ n
node/4.9.1
ο node/8.11.3
node/10.15.0
Use up/down arrow keys to select a version, return key to install, q to quit
(You can also use j and k to navigate up or down without using arrows.)
If the active node version does not change after install, try opening a new shell in case seeing a stale version.
Specifying Node Versions
There are a variety of ways of specifying the target node version for n commands. Most commands use the latest matching version, and n ls-remote lists multiple matching versions.
Numeric version numbers can be complete or incomplete, with an optional leading v.
4.9.18: 8.x.y versionsv6.1: 6.1.x versions
There are labels for two especially useful versions:
lts: newest Long Term Support official releaselatest,current: newest official release
There is support for release streams:
argon,boron,carbon: codenames for LTS release streams
The last form is for specifying other releases available using the name of the remote download folder optionally followed by the complete or incomplete version.
chakracore-release/latestnightlytest/v11.0.0-test20180528rc/10
Removing Versions
Remove some cached versions:
n rm 0.9.4 v0.10.0
Removing all cached versions except the current version:
n prune
Remove the installed node and npm (does not affect the cached version). This can be useful to revert to the system version of node (if in a different location), or if you no longer wish to use node and npm, or are switching to a different way of managing them.
n uninstall
Using Downloaded Node Versions Without Reinstalling
There are three commands for working directly with your downloaded versions of node, without reinstalling.
You can show the path to the downloaded version:
$ n which 6.14.3
/usr/local/n/versions/6.14.3/bin/node
Or run a downloaded node version with the n run command:
n run 8.11.3 --debug some.js
Or execute a command with PATH modified so node and npm will be from the downloaded node version.
(NB: this npm will be working with a different and empty global node_modules directory, and you should not install global
modules this way.)
n exec 10 my-script --fast test
Miscellaneous
Command line help can be obtained from n --help.
List matching remote versions available for download:
n ls-remote lts
n ls-remote latest
n lsr 10
n --all lsr
List downloaded versions in cache:
nvh ls
Display diagnostics to help resolve problems:
nvh doctor
Custom Source
If you would like to use a different node mirror which has the same layout as the default https://nodejs.org/dist/, you can define N_NODE_MIRROR.
The most common example is users in China can define:
export N_NODE_MIRROR=https://npm.taobao.org/mirrors/node
There is also N_NODE_DOWNLOAD_MIRROR for a different mirror with same layout as the default https://nodejs.org/download
Custom Architecture
By default n picks the binaries matching your system architecture, e.g. n will download 64 bit binaries for a 64 bit system. You can override this by using the -a or --arch option.
Download and use latest 32 bit version of node:
n --arch x86 latest
Download and use 64 bit LTS version of node for older Mac Intel Core 2 Duo systems (x86 image is no longer available but x64 runs fine):
n --arch x64 lts
Optional Environment Variables
The n command downloads and installs to /usr/local by default, but you may override this location by defining N_PREFIX.
To change the location to say $HOME/.n, add lines like the following to your shell initialization file:
export N_PREFIX=$HOME/.n
export PATH=$N_PREFIX/bin:$PATH
By default n downloads archives from the mirror site which have been compressed with gzip. You can switch to using the xz compressed archives by defining N_USE_XZ.
export N_USE_XZ=true
In brief:
N_NODE_MIRROR: See Custom sourceN_NODE_DOWNLOAD_MIRROR: See Custom source- support for NO_COLOR and CLICOLOR=0 for controlling use of ANSI color codes
N_MAX_REMOTE_MATCHESto change the defaultls-remotemaximum of 20 matching versions
Current Tags
- 10.0.0 ... latest (4 months ago)
118 Versions
- 10.0.0 ... 4 months ago
- 9.2.3 ... 8 months ago
- 9.2.2 ... 8 months ago
- 9.2.1 ... 10 months ago
- 9.2.0 ... a year ago
- 9.1.0 ... 2 years ago
- 9.0.1 ... 2 years ago
- 9.0.0 ... 2 years ago
- 8.2.0 ... 3 years ago
- 8.1.0 ... 3 years ago
- 8.0.2 ... 3 years ago
- 8.0.1 ... 3 years ago
- 8.0.0 ... 3 years ago
- 7.5.0 ... 3 years ago
- 7.4.1 ... 3 years ago
- 7.4.0 [deprecated] ... 3 years ago
- 7.3.1 ... 3 years ago
- 7.3.0 ... 4 years ago
- 7.2.2 ... 4 years ago
- 7.2.1 ... 4 years ago
- 7.2.0 ... 4 years ago
- 7.1.0 ... 4 years ago
- 7.0.2 ... 4 years ago
- 7.0.1 ... 4 years ago
- 7.0.0 ... 4 years ago
- 6.8.0 ... 4 years ago
- 6.7.1 ... 4 years ago
- 6.7.0 ... 4 years ago
- 6.6.0 ... 4 years ago
- 6.5.1 ... 5 years ago
- 6.5.0 [deprecated] ... 5 years ago
- 6.4.0 ... 5 years ago
- 6.3.1 ... 5 years ago
- 6.3.0 ... 5 years ago
- 6.2.0 ... 5 years ago
- 6.1.3 ... 5 years ago
- 6.1.2 ... 5 years ago
- 6.1.1 ... 5 years ago
- 6.1.0 ... 5 years ago
- 6.0.1 ... 5 years ago
- 6.0.0 ... 5 years ago
- 6.0.0-1 ... 5 years ago
- 6.0.0-0 ... 5 years ago
- 5.0.2 ... 5 years ago
- 5.0.1 ... 5 years ago
- 5.0.0 ... 5 years ago
- 5.0.0-next.0 ... 6 years ago
- 4.1.0 ... 6 years ago
- 4.0.0 ... 6 years ago
- 3.0.2 ... 6 years ago
- 3.0.1 ... 6 years ago
- 3.0.0 ... 6 years ago
- 2.1.12 ... 7 years ago
- 2.1.11 ... 7 years ago
- 2.1.10 ... 7 years ago
- 2.1.9 ... 7 years ago
- 2.1.8 ... 7 years ago
- 2.1.7 ... 8 years ago
- 2.1.6 ... 8 years ago
- 2.1.5 ... 8 years ago
- 2.1.4 ... 8 years ago
- 2.1.3 ... 8 years ago
- 2.1.2 ... 8 years ago
- 2.1.1 ... 9 years ago
- 2.1.0 ... 9 years ago
- 2.0.2 ... 9 years ago
- 1.4.2 ... 9 years ago
- 2.0.1 ... 9 years ago
- 1.4.1 ... 9 years ago
- 2.0.0 ... 9 years ago
- 1.4.0 ... 9 years ago
- 1.3.0 ... 10 years ago
- 1.2.14 ... 10 years ago
- 1.2.13 ... 10 years ago
- 1.2.11 ... 10 years ago
- 1.2.9 ... 10 years ago
- 1.2.8 ... 10 years ago
- 1.2.7 ... 10 years ago
- 1.2.6 ... 10 years ago
- 1.2.5 ... 10 years ago
- 1.2.4 ... 10 years ago
- 1.2.3 ... 10 years ago
- 1.2.2 ... 10 years ago
- 1.2.1 ... 11 years ago
- 1.1.0 ... 11 years ago
- 1.0.0 ... 11 years ago
- 0.9.3 ... 12 years ago
- 0.9.2 ... 12 years ago
- 0.9.1 ... 12 years ago
- 0.9.0 ... 12 years ago
- 0.8.2 ... 12 years ago
- 0.8.1 ... 12 years ago
- 0.8.0 ... 12 years ago
- 0.7.3 ... 12 years ago
- 0.7.2 ... 13 years ago
- 0.7.1 ... 13 years ago
- 0.7.0 ... 13 years ago
- 0.6.1 ... 13 years ago
- 0.6.0 ... 13 years ago
- 0.5.4 ... 13 years ago
- 0.5.3 ... 13 years ago
- 0.5.2 ... 13 years ago
- 0.5.1 ... 13 years ago
- 0.5.0 ... 13 years ago
- 0.4.2 ... 13 years ago
- 0.4.1 ... 14 years ago
- 0.4.0 ... 14 years ago
- 0.3.0 ... 14 years ago
- 0.2.2 ... 14 years ago
- 0.2.1 ... 14 years ago
- 0.2.0 ... 14 years ago
- 0.1.2 ... 14 years ago
- 0.1.1 ... 14 years ago
- 0.1.0 ... 14 years ago
- 0.0.4 ... 14 years ago
- 0.0.3 ... 14 years ago
- 0.0.2 ... 14 years ago
- 0.0.1 ... 14 years ago




